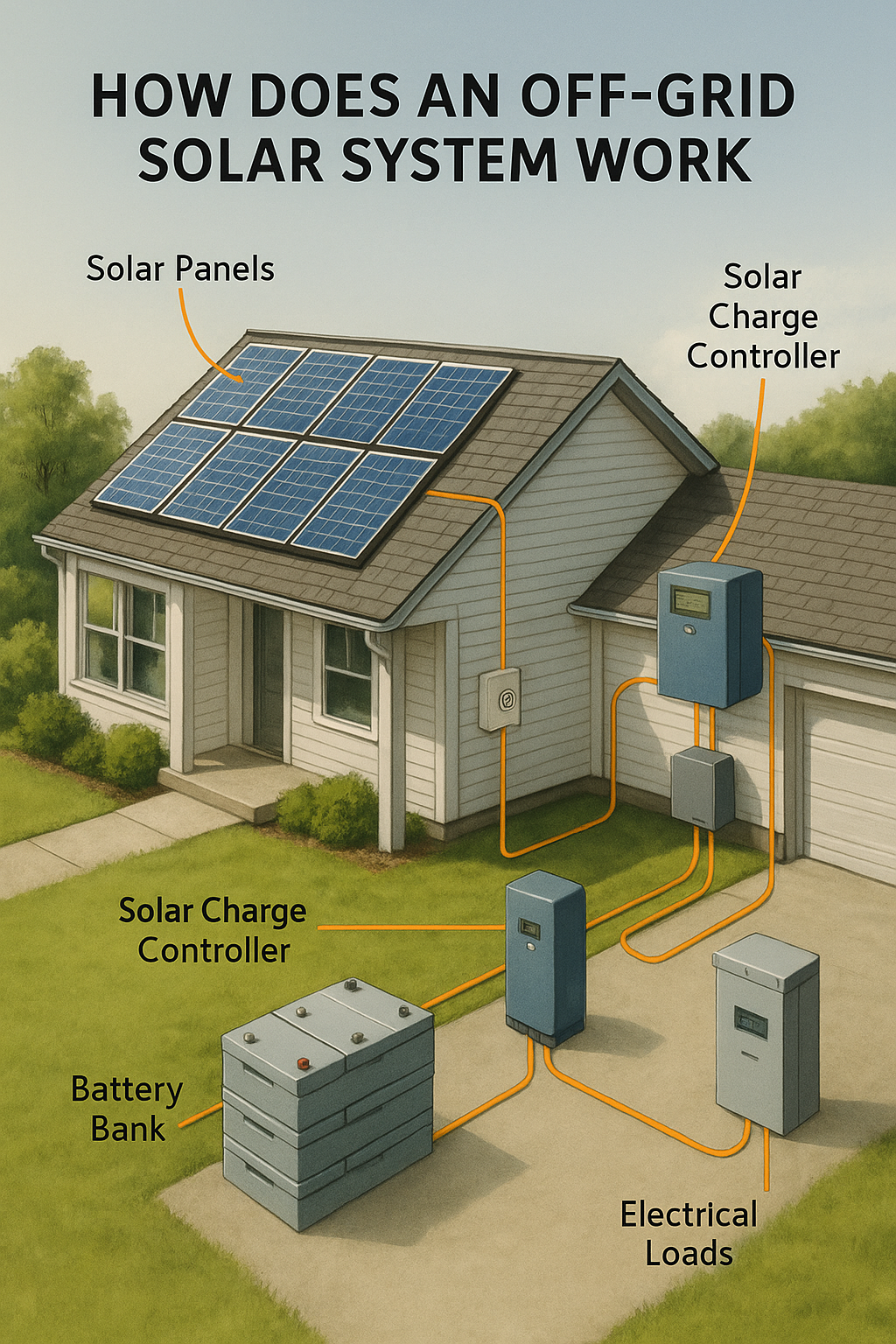
How Does an Off-Grid Solar System Work
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system is a self-sustaining energy solution that operates independently from the traditional power grid. It’s perfect for remote locations, rural properties, tiny homes, cabins, RVs, and eco-conscious users seeking energy independence. Unlike grid-tied systems, off-grid solar setups rely entirely on solar energy and battery storage to power homes, tools, appliances, and lighting.
In this guide, we’ll break down how off-grid solar systems work, their main components, and what makes them ideal for certain lifestyles and locations. We’ll also highlight common applications, benefits, and key considerations for anyone planning to go off the grid.
“? A Beginner-Friendly Guide“
A complete off-grid solar power setup includes the following essential parts:
- Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules)
These collect sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The number and size of panels depend on your energy needs and location’s sunlight exposure.
- Charge Controller
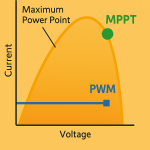
A solar charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the batteries. It prevents overcharging and optimizes charging efficiency. There are two main types:
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) – More efficient and ideal for large systems.
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) – Affordable and best for small-scale setups.
- Battery Bank
This is where energy is stored for use when the sun isn’t shining (nighttime, cloudy days). Common battery types include:
- Lithium-ion – Long-lasting, efficient, low maintenance
- AGM/Gel lead-acid – Lower cost, sealed, maintenance-free
- Flooded lead-acid – Economical but requires regular maintenance
- Inverter
An inverter converts DC electricity stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC), which most household appliances use. Pure sine wave inverters offer clean, stable power.
- Backup Generator (Optional)
Some off-grid systems include a backup generator to charge batteries during extended cloudy periods or for emergency loads.
Off-Grid vs Grid-Tied Solar System Comparison
Feature | Off-Grid Solar System | Grid-Tied Solar System |
Grid Dependency | Completely independent | Connected to the utility grid |
Battery Storage | Required for power storage | Optional (net metering often used instead) |
Power Availability | 24/7 if batteries are sized correctly | Only during grid uptime unless paired with storage |
Setup Cost | Higher upfront (batteries, inverters, etc.) | Generally lower (fewer components) |
Monthly Utility Bills | None | Still receive bills (may be reduced) |
Best For | Remote locations, energy independence | Urban/suburban homes, grid support |
Backup Generator Needed | Often included for emergencies | Usually not necessary |
Energy Management | Manual or smart monitoring required | Can export excess to grid automatically |
This table provides a quick comparison to help determine which solar system best fits your goals, location, and energy priorities.
Top Benefits of an Off-Grid Solar System
Choosing an off-grid solar system isn’t just a lifestyle preference—it’s a strategic move toward self-sufficiency and long-term cost reduction. Here’s a deeper look at its most compelling benefits:
- Energy Independence: Generate and store your own electricity without relying on utility companies. Ideal for remote or disaster-prone regions where grid power is unstable or unavailable.
- No Utility Bills: Off-grid systems eliminate recurring monthly charges. While the initial investment can be higher, the system typically pays for itself within a few years through long-term savings.
- Remote Access and Reliability: Perfect for isolated locations—cabins, farms, islands, or mobile setups—where grid extension is too costly or impractical. Solar energy paired with battery storage ensures 24/7 power availability.
- Environmentally Friendly: Off-grid systems use 100% renewable energy. By reducing fossil fuel dependence, users can cut their carbon footprint and support global climate goals.
- Customizable and Scalable: Start with a basic setup and expand as your energy needs grow. Modular design allows users to add more panels, batteries, or even hybrid backup generators over time.
- Low Operating Costs: After installation, maintenance is minimal—especially with lithium battery banks and modern MPPT controllers. No monthly service fees or rising energy tariffs.
Off-Grid Battery Comparison
Battery Type | Cycle Life | Depth of Discharge | Efficiency | Maintenance | Cost | Best For |
Lithium-Ion | 5,000–10,000 | 90–100% | 90–95% | None | $$$$$ | Full off-grid homes, mobile solar setups |
AGM Lead-Acid | 500–1,000 | 50–70% | 80–85% | Low | $$ | Budget builds, simple solar installations |
Gel Lead-Acid | 500–1,200 | 50–80% | 85–88% | Low | $$ | Indoor setups, moderate usage |
Flooded Lead-Acid | 300–1,000 | 30–50% | 75–85% | High | $ | Large setups with regular maintenance |
Top Benefits of an Off-Grid Solar System
Choosing an off-grid solar system isn’t just a lifestyle preference—it’s a strategic move toward self-sufficiency and long-term cost reduction. Here’s a deeper look at its most compelling benefits:
- Energy Independence: Generate and store your own electricity without relying on utility companies. Ideal for remote or disaster-prone regions where grid power is unstable or unavailable.
- No Utility Bills: Off-grid systems eliminate recurring monthly charges. While the initial investment can be higher, the system typically pays for itself within a few years through long-term savings.
- Remote Access and Reliability: Perfect for isolated locations—cabins, farms, islands, or mobile setups—where grid extension is too costly or impractical. Solar energy paired with battery storage ensures 24/7 power availability.
- Environmentally Friendly: Off-grid systems use 100% renewable energy. By reducing fossil fuel dependence, users can cut their carbon footprint and support global climate goals.
- Customizable and Scalable: Start with a basic setup and expand as your energy needs grow. Modular design allows users to add more panels, batteries, or even hybrid backup generators over time.
- Low Operating Costs: After installation, maintenance is minimal—especially with lithium battery banks and modern MPPT controllers. No monthly service fees or rising energy tariffs.
Common Applications of Off-Grid Solar
Off-grid solar systems are versatile and can be used in a wide range of real-world scenarios where grid power is inaccessible, unreliable, or undesired. Here are some of the most common and impactful applications:
- Remote homes and off-grid residences: From mountain cabins to rural farms, off-grid systems enable self-reliant living without needing grid infrastructure.
- Tiny houses and mobile living setups: Minimalist homes, converted vans, and RVs can use compact solar kits for lighting, refrigeration, and device charging.
- Agricultural operations: Farms benefit from solar-powered irrigation systems, electric fencing, water pumps, and off-grid storage barns.
- Island and coastal communities: Off-grid solar is ideal for areas where running traditional power lines is cost-prohibitive or logistically difficult.
- Emergency preparedness and disaster relief: Off-grid systems provide essential backup power during hurricanes, wildfires, or blackouts.
- Telecom and remote monitoring stations: Communications infrastructure in isolated areas can rely on solar to power antennas, cameras, and sensors.
- Recreational and outdoor structures: Boats, sheds, and hunting cabins use solar power for lighting, radios, and small appliances.
Off-Grid Power Explained
Off-grid power refers to energy systems that operate independently of the main electrical grid. These systems are essential for remote areas or users who want complete energy independence. They typically rely on solar panels, batteries, and sometimes generators to create a standalone energy solution. Off-grid power systems are ideal for rural properties, disaster zones, cabins, or eco-conscious users who want to eliminate reliance on utility providers.
Off-Grid Solar Battery
Off-grid solar battery are the backbone of any standalone solar power system. They store electricity generated during sunny periods for use at night or during poor weather. Common types include lithium-ion (most efficient and long-lasting), AGM (sealed and low-maintenance), and flooded lead-acid (cost-effective but maintenance-intensive). Proper battery sizing ensures your system remains functional throughout the year.
Solar Energy Storage for Off-Grid Living
Solar energy storage refers to the batteries that hold power generated by your solar panels. In off-grid applications, storage is vital to ensure uninterrupted electricity. Advanced battery management systems help optimize charging and discharging to extend battery life. Choosing the right storage capacity is essential for consistent energy availability during low-sunlight periods.
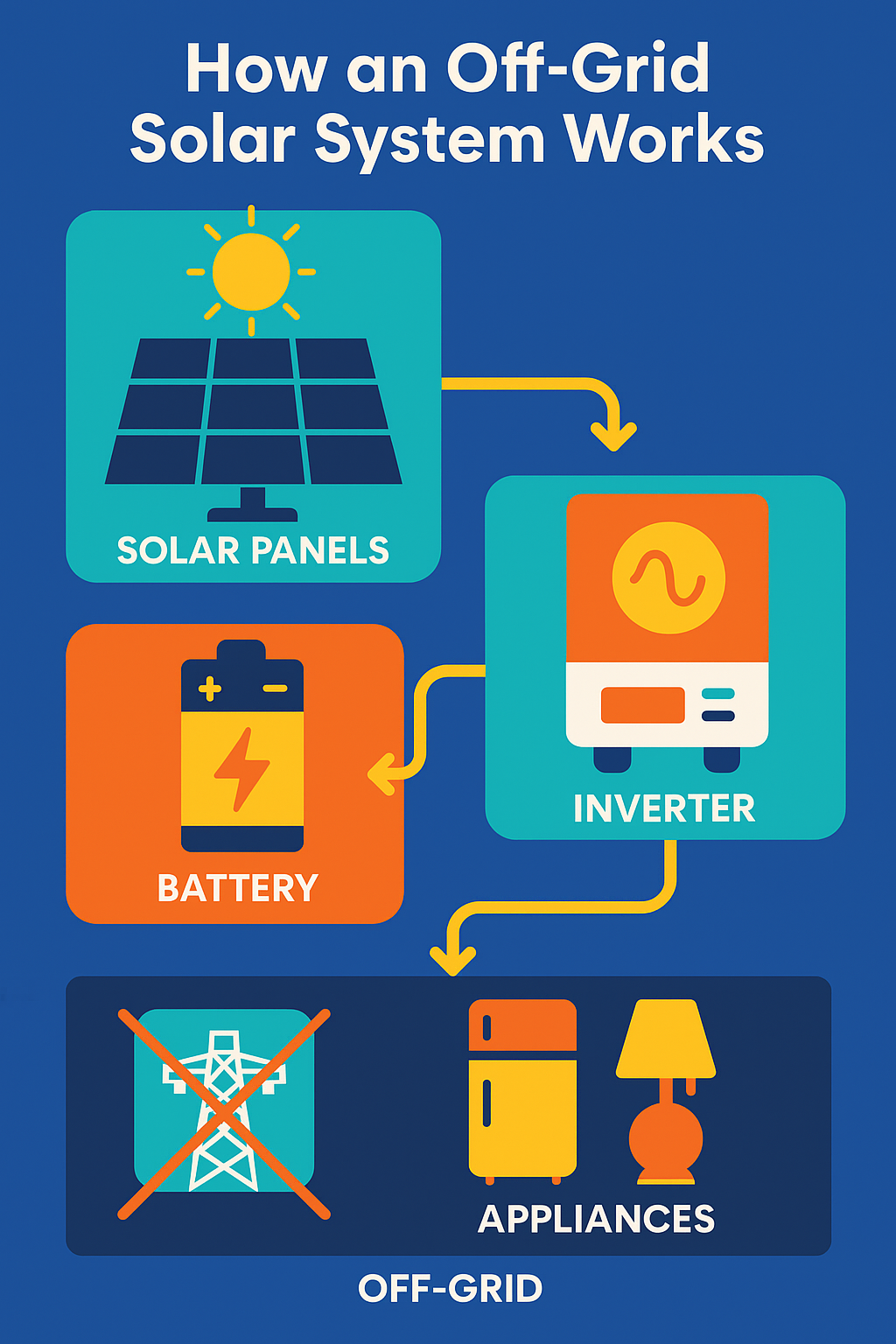
What Makes a Solar Off-Grid System Unique?
A solar off-grid system is self-contained and functions independently from public utilities. It combines solar generation, battery storage, and an inverter to support full-time power use. Unlike hybrid or grid-tied systems, off-grid setups require careful energy budgeting and backup planning, but they also offer unmatched autonomy.
What Is Remote Solar Power?
Remote solar power describes off-grid energy systems located far from utility infrastructure. These systems are designed to be durable, weather-resistant, and low-maintenance. They’re commonly used in wilderness cabins, island communities, remote outposts, and field monitoring stations. They help reduce the need for expensive diesel delivery or grid extension.
Solar Battery Storage and Why It Matters
Solar battery storage allows users to store excess solar energy for later use. For off-grid homes, it is the key to ensuring 24/7 electricity. Battery storage improves system efficiency, enhances energy security, and reduces the need for backup generators. With advancements in lithium technology, solar battery systems now last longer and perform better, even in extreme climates.
Is Off-Grid Solar Right for You?
If you live in a remote area or want energy freedom, an off-grid solar system is a reliable and eco-conscious solution. By combining solar panels, a battery bank, inverter, and charge controller, you can power your life without relying on the grid.
Before you begin, evaluate your energy needs, sun exposure, and installation site. With proper planning, you can build a powerful and sustainable off-grid solar system that pays for itself over time and reduces your carbon footprint.
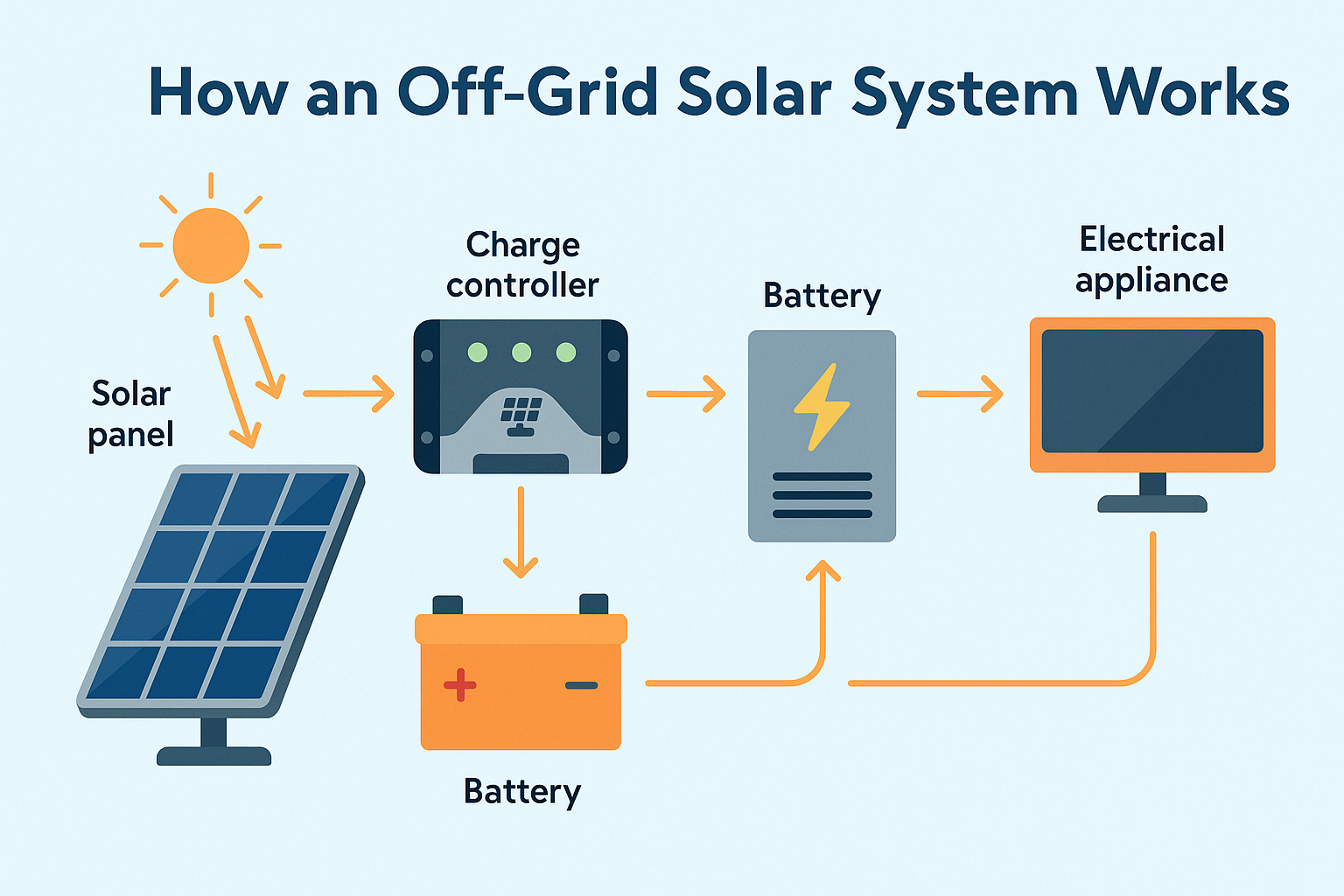
How Does an Off-Grid Solar System Work? Step-by-Step
Step 1: Solar Power Generation
Solar panels, installed in direct sunlight, absorb solar radiation and convert it into DC electricity. The amount of energy generated is influenced by factors like panel efficiency, tilt angle, shading, and the number of peak sun hours available per day.
Step 2: Power Regulation
The DC electricity produced is routed through a solar charge controller. This device regulates voltage and current to ensure batteries are charged optimally without being overcharged or damaged. Advanced systems use MPPT controllers, which maximize power conversion even under variable conditions.
Step 3: Energy Storage
Energy flows from the charge controller into a battery bank, where it is stored for later use. During the day, excess solar energy charges the batteries. At night or during poor weather, your stored energy becomes the primary power source.
Step 4: Power Conversion
Since most household appliances require AC electricity, the DC energy from the batteries passes through an inverter. The inverter converts it to a stable, usable AC current for powering lighting, electronics, refrigerators, and more.
Step 5: Energy Use and Monitoring
Electricity is now available for your daily needs. Many systems feature smart monitors or mobile apps that track power generation, battery status, and consumption in real time. These tools help optimize system performance and prevent unexpected power shortages.
Step 6: Backup Support (if available)
In the event of prolonged cloudy weather or excessive energy demand, an optional backup generator can recharge the battery bank or supply AC power directly to essential loads. This ensures continuous operation even when solar resources are temporarily limited.
Related Posts
2 Comments
-
This explanation helps demystify off-grid setups for people considering energy independence. I’m curious how these systems handle long periods of cloudy weather—do most users typically include a backup generator?
Comments are closed.










4o Image API
Nice summary of off-grid systems! I’ve always wondered how battery storage capacity is sized in relation to typical household energy use—might be worth diving into in a future post.