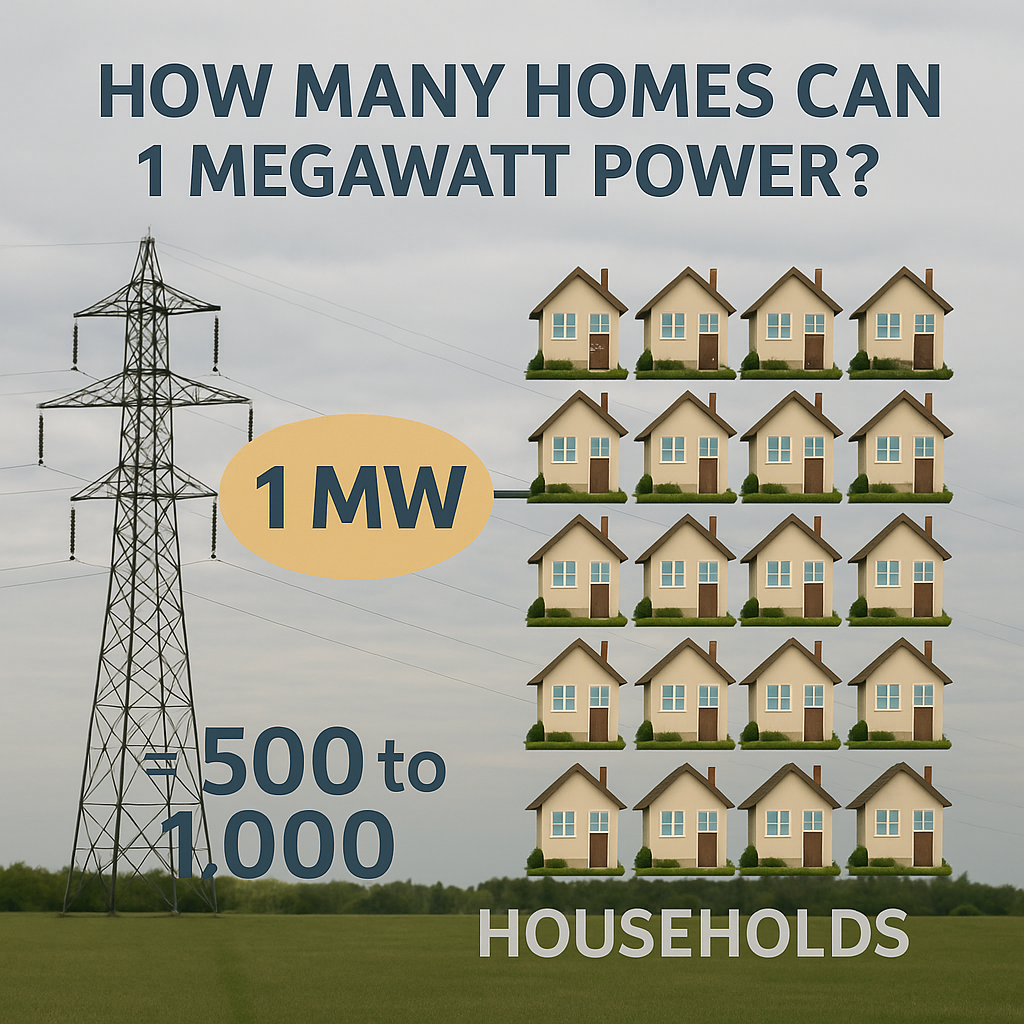
How Many Homes Can 1 Megawatt Power?
Understanding the Power of 1 Megawatt Energy
In an era of rapid energy transition, understanding electricity capacity is more important than ever. Whether you’re curious about renewable energy projects, evaluating a solar charging station, or planning a solar irrigation system, you might ask: how many homes can 1 megawatt power?
This comprehensive guide breaks it down in simple terms, explores the factors involved, and explains how 1 megawatt (MW) is used across different energy technologies
“Discover how many homes 1 megawatt (MW) can power“
What is a Megawatt?
A megawatt equals 1,000 kilowatts or 1 million watts. It’s a unit of power that describes how much energy is produced or consumed at a given moment. To understand what 1 megawatt can do, we need to compare it to typical household energy usage.
How Much Energy Does One Home Use?
In the United States, the average home uses around 10,500 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year, which equals about 1.2 kilowatts (kW) of continuous power. Based on this average:
1 megawatt can power approximately 750 to 1,000 homes at once.
However, this figure depends on many variables, including climate, local energy habits, and appliance efficiency. In warmer regions or energy-conscious communities, 1 megawatt may serve more homes.
Factors That Influence the Number of Homes Powered by 1 Megawatt
- Energy Consumption Patterns
High-energy households with electric heating, air conditioning, and large appliances will reduce the total number of homes served.
- Energy Source and Capacity Factor
Different renewable energy projects operate at different capacity factors:
- Solar: 20–25%
- Wind: 30–40%
- Natural Gas or Coal: 80–90%
For solar, 1 megawatt of installed capacity doesn’t mean it’s generating full power all day. Instead, output varies with sunlight.
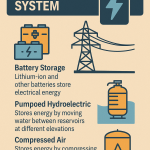
- Grid Losses and Battery Storage
Transmission losses and the presence (or absence) of battery systems can affect how much usable electricity reaches homes.
How 1 Megawatt Powers Real-World Applications
Residential Neighborhoods
On average, 1 megawatt of consistent energy supply could serve a small suburban neighborhood or rural community.
Solar Charging Stations
A solar charging station equipped with a 1MW solar array can power:
- Over 300 Level 2 EV chargers daily
- 30–50 DC fast chargers
- Facility lighting and amenities
These stations reduce strain on the grid and support clean transportation initiatives.
Solar Irrigation Systems
A solar irrigation system with a 1 megawatt power source can:
- Pump millions of gallons of water daily
- Irrigate hundreds of acres of farmland
- Support precision agriculture and reduce diesel fuel use
These systems help farmers cut costs while adopting cleaner practices.
Commercial and Agricultural Sites
1 megawatt can support:
- A medium-sized factory or warehouse
- Cold storage units
- Aquaculture farms
- Greenhouses and crop-drying facilities
1 Megawatt in Renewable Energy Projects
Benefits of Knowing How Much 1 Megawatt Can Do
- Planning efficient energy use
- Sizing off-grid systems
- Budgeting for renewable energy projects
- Understanding carbon offset potential
- Designing utility-scale systems for communities
Whether you’re designing a solar charging station or installing a solar irrigation system, knowing the capabilities of 1 megawatt ensures smarter investment and better outcomes.
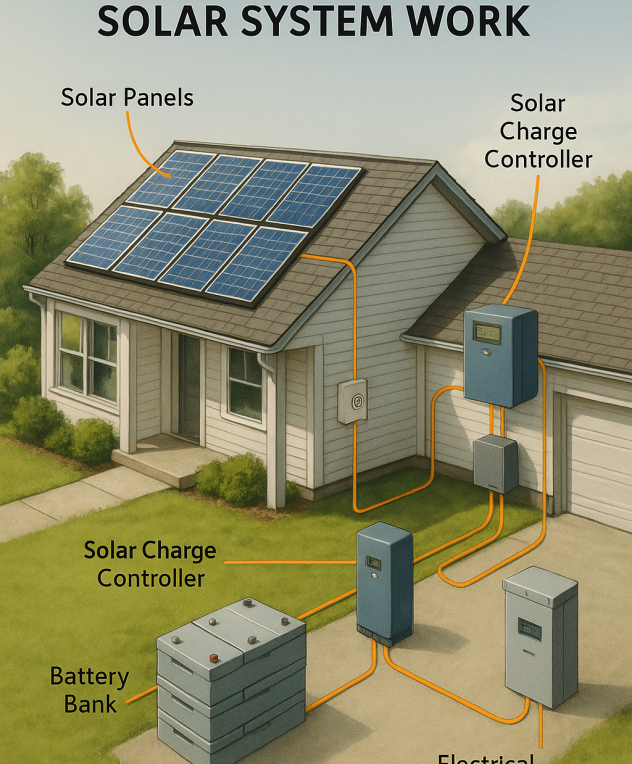
Solar Energy
In solar installations, a 1 megawatt solar farm typically consists of 3,000 to 4,000 solar panels and requires about 4–6 acres of land. Under ideal conditions, it produces about 1.5 million kWh annually—enough for about 150 homes.
Wind Energy
A single 1MW wind turbine can generate between 2.4–3 million kWh annually, depending on wind conditions. This would serve about 250–300 homes per year.
Hybrid Renewable Systems
Combining solar and wind under 1 megawatt capacity can increase total system reliability, especially in off-grid or rural environments
FAQs About 1 Megawatt and Energy Usage
Understanding the capabilities and applications of a 1 megawatt (MW) energy system is crucial for communities, businesses, and developers planning energy solutions. Whether it's powering a rural village, setting up a solar farm, or creating EV charging stations, 1MW of power can have a significant impact. Below, we answer some of the most common questions about the costs, uses, maintenance, and performance of 1MW energy systems to help you better plan your projects and investments.
Can 1 megawatt power an entire village?
Yes, in many regions around the world, especially in rural areas with lower energy consumption, a well-managed 1MW power system can supply enough electricity for an entire village. The ability to power a village depends on factors such as the number of homes, the types of appliances used, and the overall lifestyle and industrial activity. When combined with energy-efficient appliances, smart grid technology, and renewable integration (such as solar and wind), a 1MW system can reliably provide for hundreds of homes, small businesses, schools, and basic healthcare facilities.
How much does it cost to install a 1MW solar power system?
The cost to install a 1MW solar system can vary widely depending on geographic location, local labor costs, permitting fees, and the quality of materials used (like solar panels, inverters, and mounting structures). Generally, the installation cost ranges from $800,000 to $1.5 million. Additional costs may include land acquisition, transmission infrastructure, and optional battery storage systems. However, government incentives, tax credits, and renewable energy grants can significantly lower the final investment. In some cases, net metering programs can also help recover costs more quickly by selling excess power back to the grid.
What’s the lifespan of a 1MW solar power plant?
A 1MW solar power plant typically has a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, provided it receives regular maintenance and monitoring. While the solar panels themselves can continue to produce energy beyond 30 years, their efficiency will gradually decline. Critical components like inverters often require replacement approximately every 10 to 15 years to maintain optimal performance. Proper maintenance includes cleaning panels to remove dust and debris, checking electrical connections, monitoring system performance, and conducting occasional technical inspections to prevent downtime and maximize returns over the plant's lifetime.
Can a 1MW system run entirely off-grid?
Yes, a 1MW system can be designed to operate entirely off-grid, but doing so requires careful system planning and the integration of energy storage solutions like lithium-ion or other battery technologies. Key components needed include high-capacity battery banks, advanced inverters, and an energy management system to balance generation and consumption. Off-grid systems are essential for remote areas without access to national grids and need to be designed to store enough energy to supply electricity during nighttime and cloudy days. Backup systems such as diesel generators are sometimes used to ensure continuous reliability.
How many electric vehicles can a 1MW solar charging station serve?
A 1MW solar charging station can typically support about 300 to 500 electric vehicle (EV) charges per day, depending on the power rating of the chargers and the size of the EV batteries. For example, Level 2 chargers (around 7–22kW) can serve more vehicles with slower charging speeds, whereas fast chargers (50–150kW or higher) provide quicker charging but serve fewer vehicles per day. Station efficiency, battery buffer systems, time-of-use charging habits, and average daily sunlight also influence the total number of EVs a 1MW setup can handle. In high-demand settings, operators may combine solar power with energy storage to smooth supply during peak hours.
Related Posts
1 Comment
Comments are closed.










4o Image API
Interesting breakdown—it’s surprising how far 1 megawatt can go depending on household usage and efficiency. I’d be curious to see how this varies across regions with different average consumption patterns.