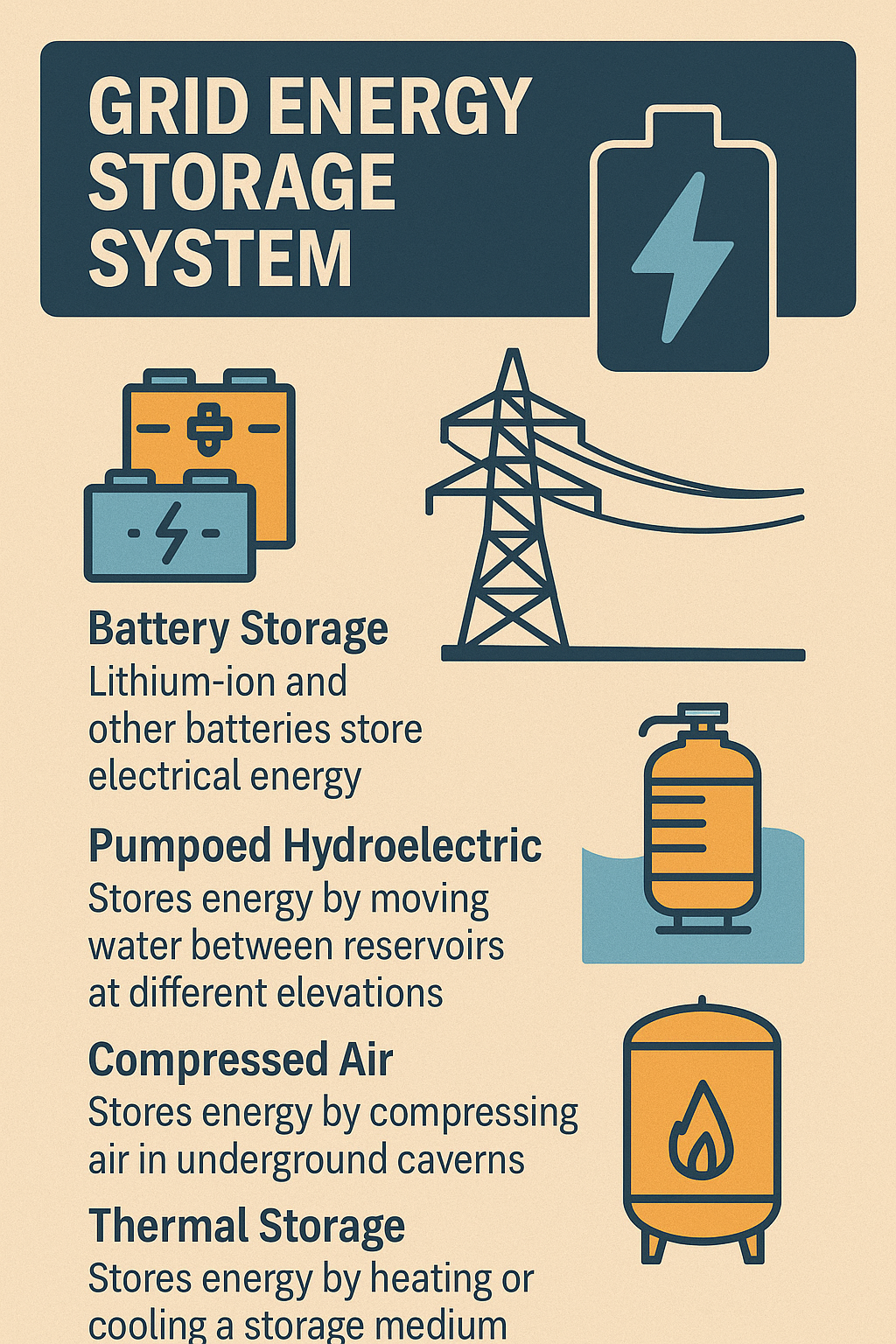
What is a Grid Energy Storage System?
Grid energy storage is one of the key technologies driving the transition to a more reliable, efficient, and sustainable power grid. As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more common, energy storage solutions are needed to stabilize supply, reduce waste, and deliver power when it’s most needed. This is where grid energy storage systems come in.
“High voltage lifepo4 lithium battery“
A grid energy storage system is a method or device that stores electricity for later use. Unlike a typical battery used in phones or laptops, grid power storage operates on a much larger scale and is directly integrated with a region’s electrical grid. These systems are designed to absorb energy when supply exceeds demand and discharge it when demand exceeds supply.
Grid energy storage can involve a variety of technologies, including batteries, pumped hydro, compressed air, and flywheels. However, battery-based systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, fast response times, and compatibility with renewable energy sources.
Why Grid Energy Storage Matters
Energy production and consumption rarely match up perfectly. For example, solar panels generate a lot of electricity during the day, but demand usually peaks in the evening. Without storage, that extra daytime energy gets wasted. Grid energy storage smooths out these imbalances by storing excess power and releasing it during high-demand periods.
In addition, energy storage improves grid reliability. It can act as a backup power source during outages, regulate voltage and frequency, and help defer expensive upgrades to transmission infrastructure.
Key Qualities of a Grid Energy Storage System
- Capacity and Scalability
Grid energy storage systems need to handle massive volumes of electricity. This is measured in megawatt-hours (MWh) or gigawatt-hours (GWh). A good system should be scalable, meaning it can be expanded as energy needs grow. Scalability ensures that the system remains relevant over time and can support future energy demands.
- Response Time
One of the standout qualities of modern grid energy storage systems is their fast response time. They can begin discharging electricity almost instantly when there is a sudden spike in demand or a drop in supply. This makes them ideal for maintaining grid stability and preventing blackouts.
- High Voltage Compatibility
High voltage batteries are essential in grid-scale energy storage. These batteries can store and release large amounts of energy without degrading too quickly. High voltage systems are more efficient and reduce the number of connections and components required, which simplifies system design and maintenance.
- Energy Density
Energy density refers to the amount of energy a system can store relative to its size or weight. The highest energy density battery technologies allow for more compact and efficient storage systems. This is crucial when space is limited or when transportation and installation costs need to be minimized.
- Efficiency
Efficiency measures how much energy put into storage can be retrieved later. A high-efficiency system loses little energy during the charge-discharge cycle. Technologies like lithium-ion batteries typically offer high round-trip efficiencies, often over 90%.
- Longevity and Cycle Life
A grid power storage system must withstand thousands of charge and discharge cycles over many years. The cycle life depends on the battery technology used. Lithium-ion batteries, for instance, can last between 3,000 to 10,000 cycles depending on their design and usage.
- Safety and Reliability
Safety is non-negotiable in grid-scale applications. These systems must be able to operate reliably under various conditions without posing risks to people or infrastructure. This includes thermal stability, fire resistance, and robust control systems to manage performance.
Types of Grid Energy Storage Technologies
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Currently, lithium-ion is the most widely used battery technology in grid energy storage. It offers a good balance of energy density, efficiency, and cost. It is also relatively easy to scale.
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes that circulate through the system. They have lower energy density but are easy to scale and have a long cycle life, making them a strong contender for grid power storage.
Solid-State Batteries
Still in development for large-scale use, solid-state batteries promise even higher energy densities and improved safety over lithium-ion. They may soon become the highest energy density battery solution for grid applications.
Pumped Hydro Storage
This traditional method uses gravity to store energy. Water is pumped to a higher elevation during low demand and released through turbines during peak demand. It has a high efficiency but requires specific geographic conditions.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
This system stores energy by compressing air into underground caverns. The air is released to drive turbines when electricity is needed. It is best suited for long-duration storage.
Flywheels
Flywheels store energy in the form of rotational kinetic energy. They have a fast response time and long life but are typically used for short-duration storage.
Benefits of Grid Scale Energy Storage
Benefits of Grid Scale Energy Storage
- Renewable Energy Integration
Grid-scale energy storage allows intermittent sources like wind and solar to become reliable parts of the energy mix. It captures excess generation and releases it when needed, ensuring a steady power supply.
- Grid Stability and Flexibility
Storage helps balance supply and demand, manage voltage levels, and provide reserve power. It enhances the flexibility of the grid, allowing it to respond dynamically to changes.
- Peak Shaving and Load Shifting
During peak demand, stored energy can be used to avoid drawing expensive power from peaker plants. This process, known as peak shaving, lowers costs and reduces strain on the grid.
- Deferred Infrastructure Investments
Energy storage can delay or reduce the need for costly grid upgrades, such as new power lines or substations. This can save utilities and customers a significant amount of money.
- Environmental Impact
By enabling greater use of renewable energy and reducing the need for fossil fuel-based peaker plants, grid energy storage contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, implementing grid energy storage comes with challenges:
- Cost: Upfront costs can be high, especially for advanced battery technologies.
- Lifespan: Degradation over time can impact performance and require replacement.
- Recycling and Disposal: Safe disposal or recycling of battery materials is a growing concern.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Many regions lack clear policies or incentives for grid-scale storage deployment.
The Future of Grid Energy Storage
Innovation is rapidly transforming the landscape of grid power storage. Research is underway to improve battery chemistries, reduce costs, and enhance safety. The push for the highest energy density battery is driving breakthroughs that could make storage even more compact and efficient.
As energy systems evolve, we can expect to see hybrid solutions combining different storage technologies to take advantage of their unique strengths. For instance, pairing high voltage batteries with long-duration storage systems like CAES or flow batteries.
Public and private investments in grid scale energy storage are also growing. Governments around the world are introducing incentives and policies to accelerate deployment. This momentum will likely continue as the world moves toward a more resilient and sustainable energy future.A grid energy storage system is a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure. It enables the reliable use of renewable energy, enhances grid stability, and offers economic and environmental benefits. With ongoing innovation in high voltage batteries and the race for the highest energy density battery, the capabilities of grid scale energy storage are expanding rapidly.
For utilities, policymakers, and communities alike, understanding and investing in grid power storage is not just an option—it’s a necessity for a cleaner, smarter energy future.
FAQs About Grid Energy Storage
This guide explores what grid energy storage means, how it works, the technologies behind it—including high voltage batteries and the highest energy density battery innovations—and how utilities, businesses, and communities are adopting grid power storage at scale.
What is the main purpose of grid energy storage?
To balance energy supply and demand, support renewable energy integration, reduce grid instability, and increase overall grid flexibility.
How long can grid storage systems provide power?
The duration varies widely by technology: lithium-ion battery systems typically offer 1–4 hours, flow batteries can last 6–12 hours, and pumped hydro may provide power for several days, depending on capacity.
Are grid storage systems safe?
Yes, modern grid battery storage solutions are designed with multi-layered safety protocols including fire suppression, thermal management, and real-time monitoring. LiFePO4 and solid-state battery chemistries are especially known for their thermal stability.
How does grid storage reduce costs?
By storing energy during off-peak times when prices are low and using it during peak periods when prices spike, businesses and utilities can reduce electricity bills and avoid peak demand charges.
Can businesses use grid energy storage?
Absolutely. Businesses benefit through lower energy costs, improved sustainability scores, backup power during outages, and opportunities to participate in demand response programs.
What is grid scale energy storage?
Grid scale energy storage refers to large-capacity storage installations that provide services directly to the energy grid. These systems store electricity in megawatts or gigawatts and are used by utilities to stabilize the electric power grid.
Which battery has the highest energy density?
Currently, solid-state batteries and certain advanced lithium battery chemistries are being developed as the highest energy density battery types. These can store more energy per kilogram and occupy less space, making them ideal for both EVs and grid storage.
How does grid power storage differ from home battery systems?
Grid power storage is designed for system-wide impact, handling massive electricity volumes to balance and stabilize the grid. In contrast, home battery systems serve individual users with limited backup or time-of-use optimization capabilities.
What are the maintenance needs of grid energy storage systems?
Maintenance varies by technology. Lithium-ion systems require periodic software updates and inspections; flow and CAES systems may require more hands-on mechanical maintenance. Smart systems reduce manual labor with automated alerts and predictive diagnostics.
Is grid storage essential for a 100% renewable energy future?
Yes. Because solar and wind are intermittent, grid energy storage systems are essential to store excess generation and release it when these sources are unavailable, enabling a stable, renewable-powered grid.
Related Posts
1 Comment
Comments are closed.













Runway API
This is a great introduction toGrid Energy Storage Comment why grid energy storage is becoming essential as we integrate more renewables into the power mix. One aspect I’d love to see explored further is how different storage technologies (like lithium vs. flow batteries) compare in large-scale applications—especially when it comes to balancing cost, scalability, and lifecycle.