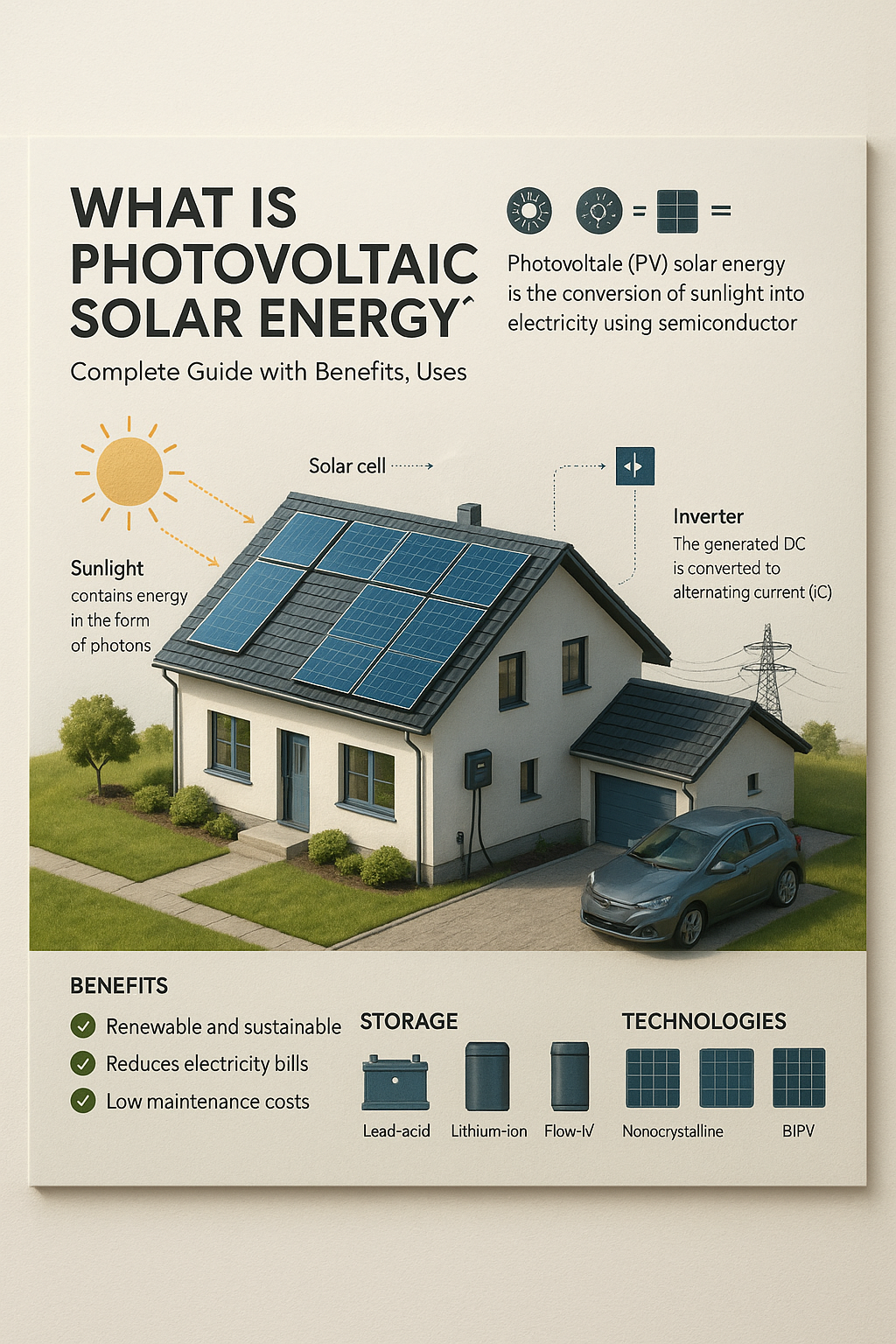
What Is Photovoltaic Solar Energy?
Tapping Into the Power of the Sun
In the age of sustainability and green innovation, photovoltaic solar energy has emerged as a cornerstone of clean power generation. As governments, businesses, and homeowners search for reliable, renewable energy alternatives, the demand for solar panel systems, residential solar installations, and solar power technology continues to grow.
But what exactly is photovoltaic solar energy, and why is it such a game changer in the world of renewable energy? This blog explains the core concepts, technologies, applications, and benefits of photovoltaic (PV) energy in simple, clear language.
“
Complete Guide with Benefits, Uses & Technologies
“
Photovoltaic solar energy is the conversion of sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels composed of photovoltaic cells. These cells are usually made of semiconductor materials like silicon. When exposed to sunlight, they generate direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
The energy can be used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed into the electric grid via inverters that convert DC to alternating current (AC).
How Photovoltaic Systems Work
A basic photovoltaic system includes:
- Solar panels (PV modules)
- Inverter (DC to AC conversion)
- Mounting structure
- Battery storage (optional)
- Monitoring system
When sunlight hits the solar panel, the photovoltaic cells absorb the photons and release electrons, generating electricity. This clean energy can be used to power homes, commercial buildings, or charge electric vehicles.
Types of Photovoltaic Systems
- Grid-Tied Photovoltaic Systems
- Most common and cost-effective PV setup
- Connected directly to the utility grid
- Allows for net metering: excess energy sent to the grid earns credits
- No battery storage; relies on the grid when solar production is low
- Off-Grid Photovoltaic Systems
- Operate independently of the grid
- Require battery storage and backup generators for reliability
- Ideal for remote or rural areas without grid access
- Enables total energy independence
- Hybrid Photovoltaic Systems
- Combine grid connection with battery storage
- Store solar energy for use during outages or peak times
- Provide backup power while still enjoying net metering benefits
- Popular among homeowners looking for both savings and resilience—
Benefits of Photovoltaic Solar Energy
- Renewable and Sustainable
Photovoltaic solar energy relies on the sun, an abundant and virtually inexhaustible resource. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy doesn’t deplete finite reserves or contribute to atmospheric pollution. As long as the sun shines, PV systems can continuously provide clean electricity.
- Reduces Electricity Bills
Installing a residential or commercial photovoltaic system significantly reduces reliance on the traditional utility grid. By generating your own electricity, you can drastically lower monthly bills. In many regions, net metering allows users to sell excess energy back to the grid, further boosting savings.
- Low Maintenance Costs
PV systems have no moving parts, which means they experience less wear and tear compared to mechanical energy generators. Routine maintenance involves basic panel cleaning and periodic system checks. With proper care, inverters and other system components last for decades, making PV energy a low-maintenance investment.
- Scalable and Flexible
Photovoltaic solar energy systems are modular by design, meaning they can be scaled up or down to meet specific energy needs. Whether it’s a single rooftop setup for a small home or a multi-megawatt solar farm for a city, PV technology adapts easily to the scope and budget of any project.
- Energy Independence
By generating their own electricity, users reduce dependence on centralized power grids and volatile energy markets. This is particularly valuable in remote areas or regions prone to power outages. When combined with battery storage, PV systems can function as reliable, stand-alone power sources that enhance energy security.
Common Applications of PV Solar Energy
Residential Use
- Rooftop solar panels
- Net metering to offset energy bills
- Battery storage for nighttime use
Commercial Use
- Solar-powered warehouses, schools, and factories
- Green certifications and tax incentives
Utility-Scale Solar Farms
- Thousands of panels connected to the grid
- Large-scale power generation for cities and industries
Off-Grid and Remote Areas
- Critical for areas without access to grid electricity
- Power for homes, medical centers, and communication towers
Solar-Powered Devices and Vehicles
- Solar lighting, water pumps, and chargers
- Integration with electric vehicles and solar carports
How Efficient Is Photovoltaic Energy?
The efficiency of photovoltaic solar panels depends on the technology and environment. Most PV panels convert 15–22% of sunlight into electricity. Efficiency is influenced by:
- Panel orientation and tilt
- Sunlight availability (location, weather)
- Temperature and shading
- Type of inverter used
Modern PV systems with tracking mounts and high-quality inverters can significantly increase energy yield.
Photovoltaic vs. Solar Thermal
Feature | Photovoltaic (PV) | Solar Thermal |
Output | Electricity | Heat |
Application | Homes, businesses, grid power | Water heating, space heating |
Technology | Solar panels, inverters | Mirrors, pipes, thermal tanks |
Scalability | Highly scalable | Best at medium to large scale |
Cost of Installing Photovoltaic Solar Panels
The average cost for a residential PV system in the U.S. is $2.50–$3.50 per watt. A typical 6 kW system costs about $15,000–$21,000 before incentives.
Federal tax credits and local rebates can reduce this by 30% or more.
Factors that affect cost:
- System size and brand
- Roof condition and orientation
- Installation company
- Incentives and financing options
Environmental Impact of Photovoltaic Energy
PV systems dramatically reduce carbon emissions and pollution. Over 25 years, a 5 kW residential solar system offsets:
- 100+ tons of CO₂
- Equivalent to planting 2,000+ trees
Unlike fossil fuel generation, PV systems do not produce harmful byproducts or noise.
Future of Photovoltaic Solar Energy
- Bifacial solar panels capture sunlight from both sides
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) embed solar tech into windows and walls
- Perovskite solar cells promise cheaper, flexible, higher-efficiency options
- Smart solar + battery storage systems for energy independence
As technology advances, PV energy will become even more affordable, efficient, and accessible.
Why Photovoltaic Solar Energy Is the Future
Photovoltaic solar energy is clean, renewable, and scalable—making it one of the most powerful tools in the global shift toward sustainable living. Whether for homes, businesses, or utility-scale power generation, PV systems reduce costs, increase energy security, and help combat climate change.
With ongoing advances in technology and growing global awareness, adopting photovoltaic systems is no longer just an eco-friendly decision—it’s a smart investment for the future.
Is photovoltaic energy the same as solar energy?
Photovoltaic energy is one type of solar energy. It specifically refers to the technology that converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels composed of photovoltaic cells. Solar energy, as a broader category, includes other forms such as solar thermal energy, which captures heat from the sun to warm water or air. So, while all photovoltaic energy is solar, not all solar energy is photovoltaic.
How long do photovoltaic panels last?
Photovoltaic solar panels typically last 25 to 30 years, although many continue to generate electricity beyond that period at reduced efficiency. The degradation rate is about 0.5% to 1% per year, depending on the panel quality. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and system inspections, can help extend their functional life and ensure consistent performance.
Do photovoltaic systems work on cloudy days?
Yes, photovoltaic systems can still generate electricity on cloudy or overcast days, although output will be lower compared to sunny conditions. Modern PV panels are designed to absorb both direct sunlight and diffused light. Depending on the cloud cover, output might range from 10% to 60% of their rated capacity, but they continue to function and contribute to energy needs.
Can photovoltaic systems work off-grid?
Absolutely. Off-grid PV systems are designed for locations without access to the public electricity grid. These systems typically include a battery bank to store energy generated during the day, and an inverter to convert DC to AC power. Off-grid photovoltaic systems are ideal for remote homes, cabins, agricultural operations, and emergency backup solutions where energy independence is critical.
What maintenance is required for PV panels?
Maintenance for photovoltaic systems is generally low. Key tasks include:
- Cleaning the panels every few months to remove dust, dirt, or bird droppings
- Inspecting wiring and mounting hardware annually
- Monitoring inverter performance and replacing inverters every 10–15 years
- Ensuring no tree growth or objects cast shading on the panels These routine checks help maintain optimal energy output and protect the long-term investment.
Related Posts
1 Comment
Comments are closed.












AI Quiz Generator
I think the transition to renewable energy sources like solar is key to addressing global energy challenges. Photovoltaic solar power is not only environmentally friendly, but also increasingly efficient, making it a smart choice for long-term energy solutions.